貨號
產(chǎn)品規(guī)格
售價(jià)
備注
BN40327R-100ul
100ul
¥2360.00
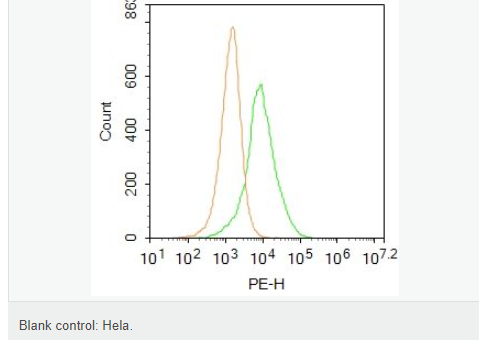
交叉反應(yīng):Human(predicted:Mouse,Rat,Chicken,Dog,Pig,Cow,Horse,Rabbit,Sheep) 推薦應(yīng)用:WB,IHC-P,IHC-F,ICC,IF,Flow-Cyt,ELISA
BN40327R-200ul
200ul
¥3490.00
交叉反應(yīng):Human(predicted:Mouse,Rat,Chicken,Dog,Pig,Cow,Horse,Rabbit,Sheep) 推薦應(yīng)用:WB,IHC-P,IHC-F,ICC,IF,Flow-Cyt,ELISA
產(chǎn)品描述
| 英文名稱 | KCTD7 |
| 中文名稱 | 鉀離子通道多聚體結(jié)構(gòu)域蛋白7抗體 |
| 別 名 | BTB/POZ domain containing protein KCTD7; EPM3; FLJ32069; Potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 7; KCTD7_HUMAN. |
| 研究領(lǐng)域 | 細(xì)胞生物 神經(jīng)生物學(xué) 通道蛋白 細(xì)胞膜受體 |
| 抗體來源 | Rabbit |
| 克隆類型 | Polyclonal |
| 交叉反應(yīng) | Human, (predicted: Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Dog, Pig, Cow, Horse, Rabbit, Sheep, ) |
| 產(chǎn)品應(yīng)用 | WB=1:500-2000 ELISA=1:5000-10000 IHC-P=1:100-500 IHC-F=1:100-500 Flow-Cyt=1ug/test ICC=1:100-500 IF=1:100-500 (石蠟切片需做抗原修復(fù)) not yet tested in other applications. optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. |
| 分 子 量 | 33kDa |
| 細(xì)胞定位 | 細(xì)胞漿 細(xì)胞膜 |
| 性 狀 | Liquid |
| 濃 度 | 1mg/ml |
| 免 疫 原 | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human KCTD7:112-180/289 |
| 亞 型 | IgG |
| 純化方法 | affinity purified by Protein A |
| 儲 存 液 | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| 保存條件 | Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. |
| PubMed | PubMed |
| 產(chǎn)品介紹 | Epilepsy affects about 0.5% of the world’s population and has a large genetic component. Epilepsy results from an electrical hyperexcitability in the central nervous system. Potassium channels are important regulators of electrical signaling, determining the firing properties and responsiveness of a variety of neurons. Benign familial neonatal convulsions (BFNC), an autosomal dominant epilepsy of infancy, has been shown to be caused by mutations in the KCNQ2 or the KCNQ3 potassium channel genes. KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 are voltage-gated potassium channel proteins with six putative transmembrane domains. Both proteins display a broad distribution within the brain, with expression patterns that largely overlap. Function: The KCTD gene family, including KCTD7, encode predicted proteins that contain N terminal domain that is homologous to the T1 domain in voltage gated potassium channels. KCTD7 displays a primary sequence and hydropathy profile indicating intracytoplasmic localization. There are two named isoforms. Subunit: May be involved in the control of excitability of cortical neurons Subcellular Location: Cell membrane. Cytoplasm, cytosol. DISEASE: efects in KCTD7 are the cause of epilepsy, progressive myoclonic 3, with or without intracellular inclusions (EPM3) [MIM:611726]. EPM3 is an autosomal recessive, severe, progressive myoclonic epilepsy with early-onset. Multifocal myoclonic seizures begin between 16 and 24 months of age after normal initial development. Neurodegeneration and regression occur with seizure onset. Other features include mental retardation, dysarthria, truncal ataxia, and loss of fine finger movements. EEG shows slow dysrhythmia, multifocal and occasionally generalized epileptiform discharges. In some patients, ultrastructural findings on skin biopsies identify intracellular accumulation of autofluorescent lipopigment storage material, consistent with neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. Note=Defects in KCTD7 are a cause of opsoclonus-myoclonus ataxia-like syndrome. Opsoclonus myoclonus ataxia syndrome (OMS) is a rare pervasive and frequently permanent disorder that usually develops in previously healthy children with normal premorbid psychomotor development and characterized by association of abnormal eye movements (opsoclonus), severe dyskinesia (myoclonus), cerebellar ataxia, functional regression, and behavioral problems. The syndrome is considered to be an immune-mediated disorder and may be tumor-associated or idiopathic. OMS is one of a few steroid responsive disorders of childhood. KCTD7 mutations have been found in a patient with an atypical clinical presentation characterized by non-epileptic myoclonus and ataxia commencing in early infancy, abnormal opsoclonus-like eye movements, improvement of clinical symptoms under steroid treatment, and subsequent development of generalized epilepsy (PubMed:22638565). Similarity: Contains 1 BTB (POZ) domain. SWISS: Q96MP8 Gene ID: 154881 Database links: Entrez Gene: 417547 Chicken Entrez Gene: 154881 Human Entrez Gene: 212919 Mouse Omim: 611725 Human SwissProt: Q5ZJP7 Chicken SwissProt: Q96MP8 Human SwissProt: Q8BJK1 Mouse Unigene: 546627 Human Unigene: 55812 Mouse Unigene: 103510 Rat Important Note: This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |